Navigating the complexities of trigonometry becomes simpler with a firm grasp of the fundamental rule that guides Sine, Cosine, and Tangent. In this article, we delve into practical applications of these rules, exploring how they facilitate solving triangles, determining unknown sides and angles, and unraveling geometric puzzles.
Mastering these rules equips you with the knowledge to tackle diverse trigonometric problems effectively.
Sine Rule
In trigonometry, the sine law, law of sines, sine rule, or sine formula is a rational equation that relates to the lengths of the sides of a triangle (any shape or kind) to the sines of its angles.
According to the sine rule,
a / sin(A) = b / sin(B) = c / sin(C)
where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of a triangle, and A, B, and C are the opposite angles.
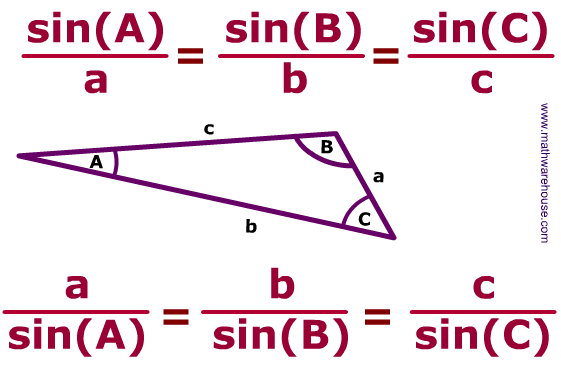
Application of Sine Rule
- Sine rule can be used to find the unknown side or length of a triangle.
- Sine rule can also be used to find the unknown angle of a triangle.
To find the unknown side or length of a triangle, three essential parameters must be provided and these parameters are:
- The angle opposite to the unknown side or length of the triangle.
- The length of a side of the triangle (b).
- Then, the angle opposite to the length of the side (b) of the triangle.
Let’s take for example we have a triangle and we want to determine the unknown side of this triangle, when the opposite angle is given, another length of the side of the triangle and its opposite angle is also given. Like the image below.
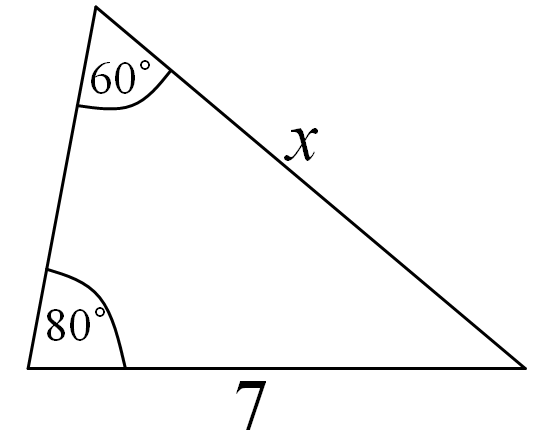
From the image above, one can see that;
The angle opposite to the unknown length of the side of the triangle is 80°. (A)
The length of the side of the triangle given is 7. (b)
Also, the angle opposite to the length of the side of the triangle given is 60° (B)
The unknown length of the side of the triangle is x. (a)
Applying the sine rule to find the value of x:
a / sin(A) = b / sin(B)
x / sin(80°) = 7 / sin(60°)
x / 0.9848 = 7 / 0.8660
Applying cross multiplication
So, x (0.8660) = 7 (0.9848)
x (0.8660) = 6.8936
Dividing both sides by 0.8660
x = 6.8936 / 0.8660
x = 7.96
Therefore, the unknown length of the side of the triangle, x is 7.96.
Read more: How to Calculate and Solve for the Area, Base and Height of a Triangle | The Calculator Encyclopedia
Using the Sine Rule When the Angle of a Triangle is Unknown
Let’s try to solve another example using the sine rule where the angle of a triangle is unknown, the opposite length of the side is given and another angle and its opposite side is also given.
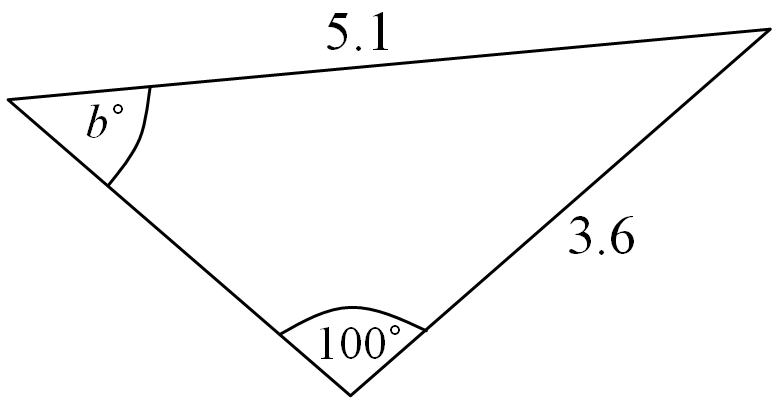
a / sin(A) = b / sin(B)
Let the unknown angle be B°
Therefore,
a = 5.1
A = 100°
b = 3.6
Where a and b represent the length of the side of the triangle and A and B represent the angle of the triangle.
5.1 / sin(100°) = 3.6 / sin(B°)
5.1 / (0.9848) = 3.6 / sin(B°)
That is, 5.1 x sin(B°) = 3.6 x 0.9848
5.1 x sin(B°) = 3.5453
sin(B°) = 3.5453 / 5.1
sin(B°) = 0.6951
B = sin-1(0.6951)
B = 44.04°
Cosine Rule
The cosine rule provides a relationship between the lengths of the sides a triangle to the cosine of its opposite angles.
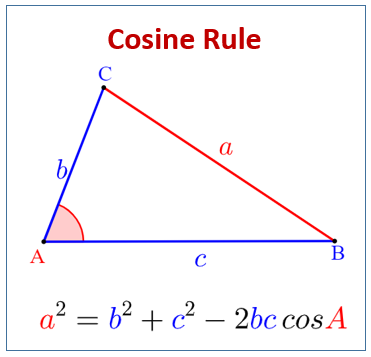
Just as is in the image, the cosine rule relates the length, a to its opposite angle, A.
a² = b² + c² – 2bc . cos(A°)
b² = a² + c² – 2ac . cos(B°)
c² = a² + b² – 2ab . cos(C°)
Applications of Cosine Rule
- Cosine rule can be used to calculate the three angles of a triangle provided the lengths of its three sides are provided.
- Cosine rule can be used to calculate the length of a side of a triangle.
Now, let’s see an example of how one can use cosine rule to compute the three angles of a triangle.
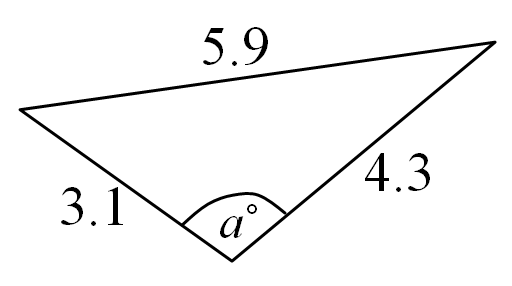
Let’s assume that
a = 5.9
b = 3.1
c = 4.3
Master Calculations Instantly
Unlock solutions for math, physics, engineering, and chemistry problem with step-by-step clarity. No internet required. Just knowledge at your fingertips, anytime, anywhere.
We would first of all calculate for angle A°
from the formulas above we know that;
a² = b² + c² – 2bc . cos(A°)
2bc . cos(A°) = b² + c² – a²
cos(A°) = (b² + c² – a²) / 2bc
Entering the Values
cos(A°) = ((3.1)² + (4.3)² – (5.9)²) / 2(3.1)(4.3)
cos(A°) = (9.61 + 18.49 – 34.81) / 26.66
That is, cos(A°) = -8.71 / 26.66
cos(A°) = -0.2517
A = cos-1(-0.2517)
A = 104.58°
Calculating for angle, B°
b² = a² + c² – 2ac . cos(B°)
2ac . cos(B°) = a² + c² – b²
cos(B°) = (a² + c² – b²) / 2ac
Entering the Values
cos(B°) = ((5.9)² + (4.3)² – (3.1)²) / 2(5.9)(4.3)
cos(B°) = (34.81 + 18.49 – 9.61) / 50.74
So, cos(B°) = 43.69 / 50.74
cos(B°) = 0.8611
B = cos-1(0.8611)
B = 30.56°
Calculating for angle, C°
c² = a² + b² – 2ab . cos(C°)
2ab . cos(C°) = a² + b² – c²
cos(C°) = (a² + b² – c²) / 2ab
Entering the Values
cos(C°) = ((5.9)² + (3.1)° – (4.3)°) / 2(5.9)(3.1)
cos(C°) = (34.81 + 9.61 – 18.49) / 36.58
Then, cos(C°) = 25.93 / 36.58
cos(C°) = 0.7089
C = cos-1(0.7089)
C = 44.86°
Side of a Triangle When the Two Sides are Given
Now, let’s calculate the length of the side of a triangle when the two other sides are given and the opposite angle of the unknown length is also given.
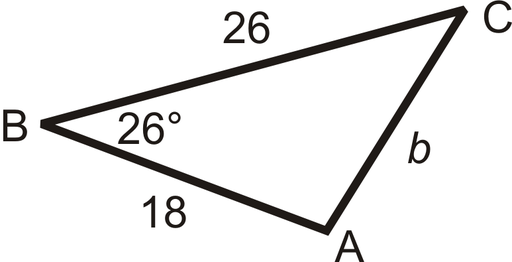
From our cosine formulas:
b² = a² + c² – 2ac . cos(B°)
where:
a = 26
c = 18
B = 26°
b² = (26)² + (18)² – 2(26)(18) . cos(26°)
b² = 676 + 324 – 2(468) . (0.8987)
So, b² = 1000 – 841.2712
b² = 158.7287
b = √(158.7287)
Therefore, b = 12.599
Tangent Rule
The tangent rule relates the tangents of two angles to the length of the opposite sides of the triangle.
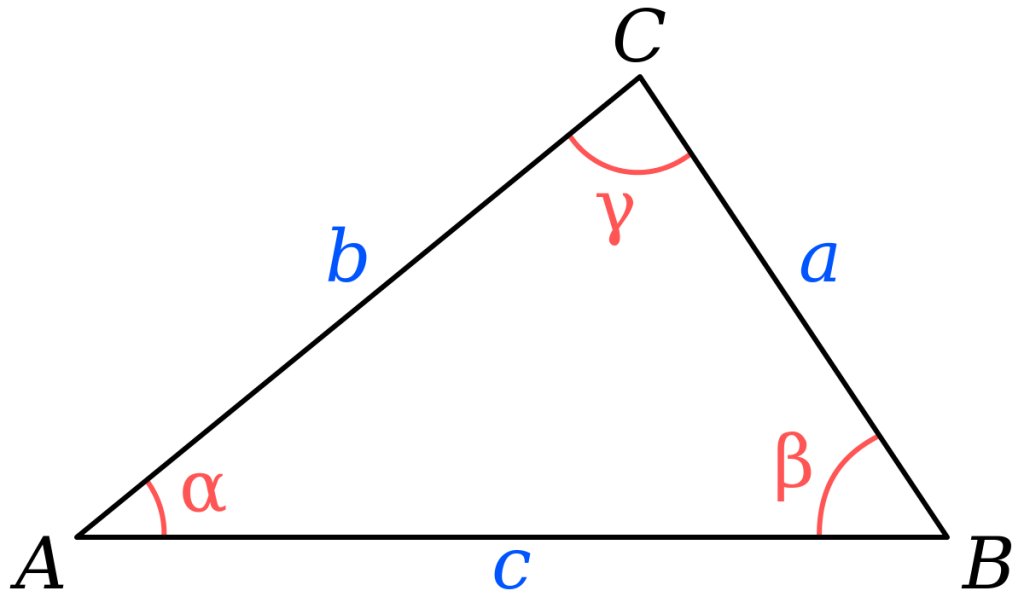
(a – b) / (a + b) = tan(A – B) / tan(A + B)
Let’s assume;
b = 10
A = 70°
B = 20°
How can we find the length of side a?
We make use of the tangent rule
(a – 10) / (a + 10) = (tan(0.5(70° – 20°))) / (tan(0.5(70° + 20°)))
(a – 10) / (a + 10) = (tan(0.5(50°))) / (tan(0.5(90°)))
So,
(a – 10) / (a + 10) = (tan(25°)) / (tan(45°))
(a – 10) / (a + 10) = (0.4663076581549986) / (0.9999999999999999)
Then,
(a – 10) / (a + 10) = 0.46630765815499864
(a – 10) = 0.46630765815499864(a + 10)
So, a – 10 = 0.46630765815499864a + 4.663076581549986
a – 0.46630765815499864a = 10 + 4.663076581549986
0.5336923418450014a = 14.663076581549987
a = 14.663076581549987 / 0.5336923418450014
Master Calculations Instantly
Unlock solutions for math, physics, engineering, and chemistry problem with step-by-step clarity. No internet required. Just knowledge at your fingertips, anytime, anywhere.
a = 27.474774194546228
Therefore, a = 27.47
Always, remember to add length units whenever you are done calculating the length of a side of a triangle.
For Example: the length of the side a of the triangle from the calculation above is 27.47 metres.
Using Nickzom Calculator to Apply Sine Rule, Cosine Rule and Tangent Rule in Trigonometry
Nickzom Calculator – The Calculator Encyclopedia is capable of calculating problems on sine rule, cosine rule and tangent rule.
To get the answer and workings of calculations on sine rule, cosine rule and tangent rule using the Nickzom Calculator – The Calculator Encyclopedia. First, you need to obtain the app.
Access the Nickzom Calculator
You can get this app via any of these means:
Web – https://www.nickzom.org/calculator-plus
To get access to the professional version via web, you need to register and subscribe for NGN 1,500 per annum to have utter access to all functionalities.
You can also try the demo version via https://www.nickzom.org/calculator
Android (Paid) – https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.nickzom.nickzomcalculator
Android (Free) – https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.nickzom.nickzomcalculator
Apple (Paid) – https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/nickzom-calculator/id1331162702?mt=8
Once, you have obtained the calculator encyclopedia app, proceed to the Calculator Map, you can either click on the cosine rule, sine rule, or tangent rule under Mathematics to solve any trigonometry calculations in need of such relationship.
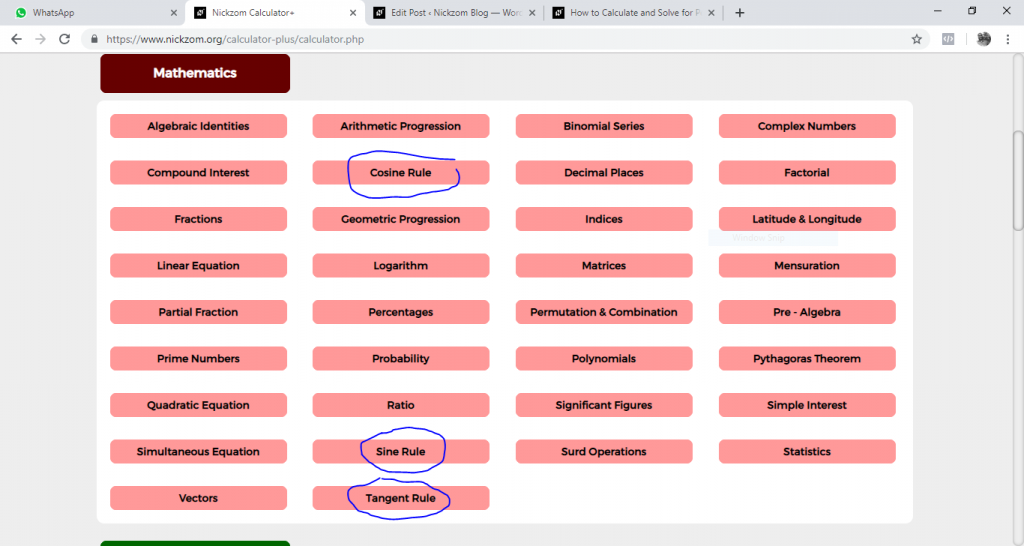
Displaying an example of how Nickzom Calculator solves for tangent rule.
First click on tangent rule, then enter the required parameters.
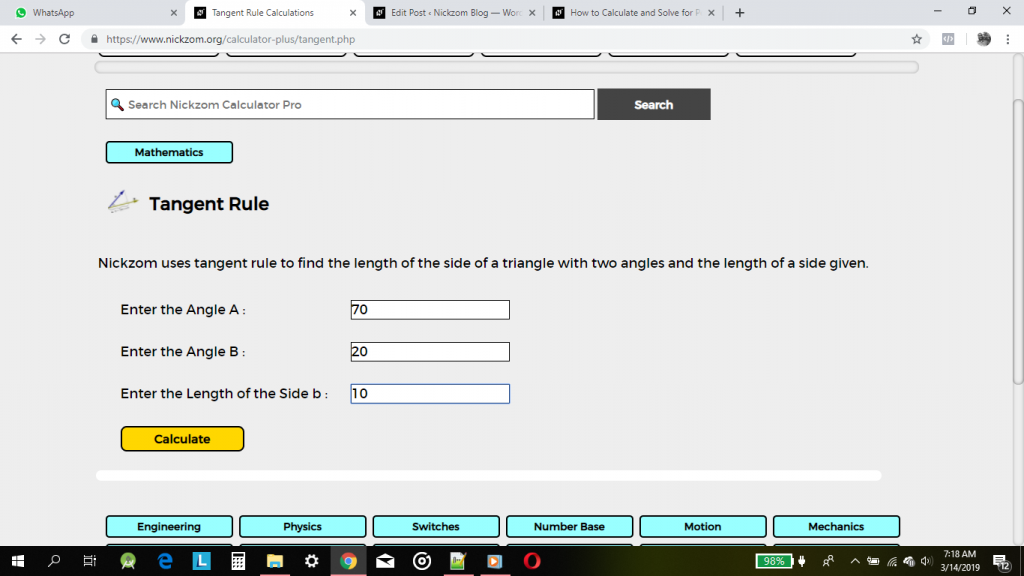
Finally, click on Calculate
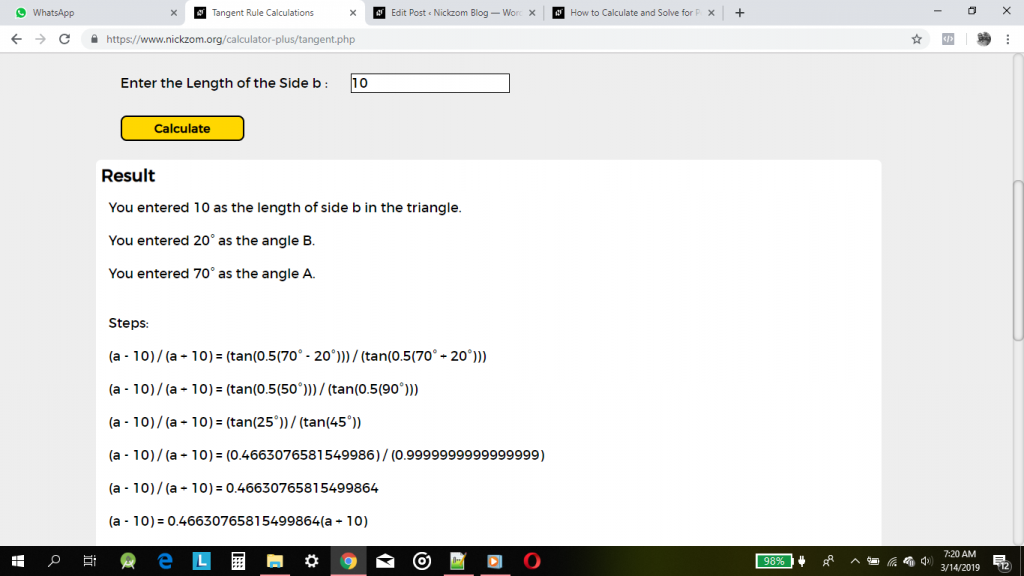
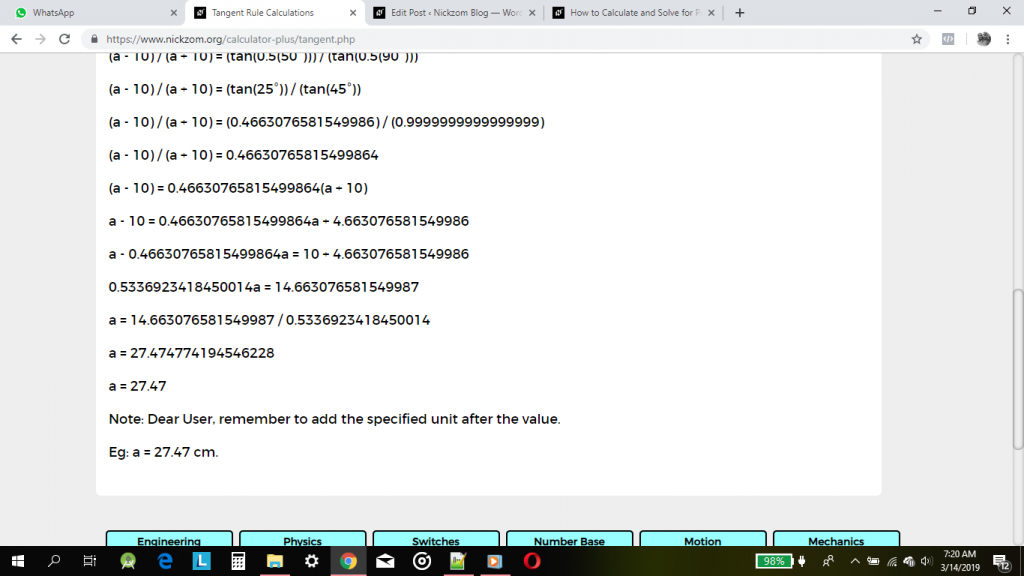
As you can see from the screenshot above, Nickzom Calculator – The Calculator Encyclopedia solves for the length of the side of a using the tangent rule and can also solve for the three angles of a triangle and the length of the side of a triangle using the cosine rule and also the length of a side of a triangle and angle of a triangle using sine rule and presents the formula, workings, and steps too.




