The solubility of polymer is represented by the image below. To calculate the solubility of polymer, two essential parameters are needed and these parameters are Concentration of Diffusing Specie in Polymer (C) and Partial Pressure (P).
The formula for calculating the solubility of polymer:
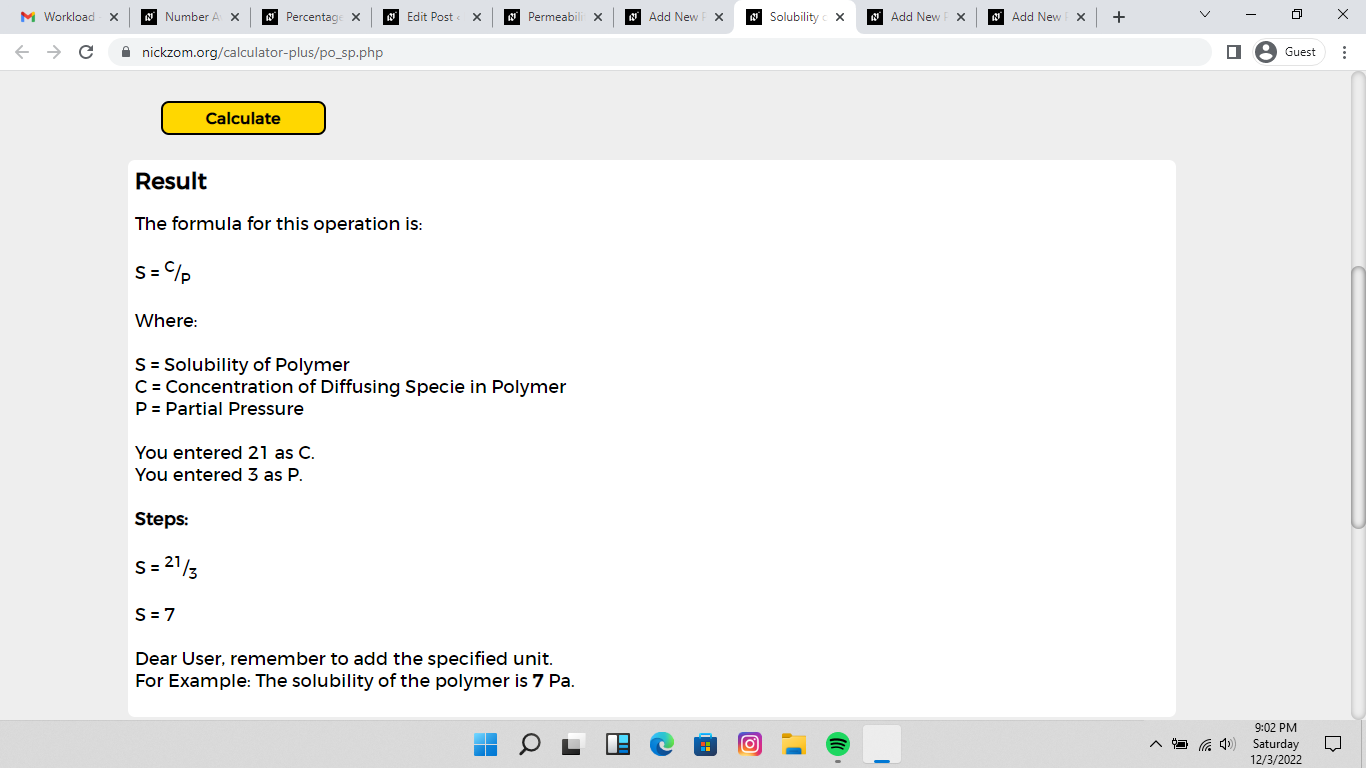
S = C/P
Where:
S = Solubility of Polymer
C = Concentration of Diffusing Specie in Polymer
P = Partial Pressure
Let’s solve an example;
Find the solubility of polymer when the concentration of diffusing specie in polymer is 21 and the partial pressure is 3.
This implies that;
C = Concentration of Diffusing Specie in Polymer = 21
P = Partial Pressure = 3
S = 21/3
S = 7
Therefore, the solubility of polymer is 7 Pa.
Calculating the Concentration of Diffusing Specie when the Solubility of Polymer and the Partial Pressure are Given
C = PS
Where:
C = Concentration of Diffusing Specie in Polymer
S = Solubility of Polymer
P = Partial Pressure
Let’s solve an example;
Find the concentration of diffusing specie in polymer when the solubility of polymer is 10 and the partial pressure is 4.
This implies that;
S = Solubility of Polymer = 10
P = Partial Pressure = 4
C = PS
So, C = 10 x 4
C = 40
Therefore, the concentration of diffusing specie is 40.
Read more: How to Calculate and Solve for Permeability Coefficient | Polymer
Calculating the Partial Pressure when the Solubility of Polymer and the Concentration of Diffusing Specie are Given
P = C / S
Where;
P = Partial Pressure
S = Solubility of Polymer
C = Concentration of Diffusing Specie in Polymer
Given an example;
Find the partial pressure when the solubility of polymer is 10 and the concentration of diffusing specie in polymer is 55.
This implies that;
S = Solubility of Polymer = 10
C = Concentration of Diffusing Specie in Polymer = 55
P = C / S
That is, P = 55 / 10
P = 5.5
Therefore, the partial pressure is 5.5.
How to Calculate the Solubility of Polymer With Nickzom calculator
Nickzom Calculator – The Calculator Encyclopedia is capable of calculating the solubility of polymer.
To get the answer and workings of the solubility of polymer using the Nickzom Calculator – The Calculator Encyclopedia. First, you need to obtain the app.
You can get this app via any of these means:
Master Calculations Instantly
Unlock solutions for math, physics, engineering, and chemistry problem with step-by-step clarity. No internet required. Just knowledge at your fingertips, anytime, anywhere.
Web – https://www.nickzom.org/calculator-plus
To get access to the professional version via web, you need to register and subscribe to have utter access to all functionalities.
You can also try the demo version via https://www.nickzom.org/calculator
Android (Paid) – https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.nickzom.nickzomcalculator
Android (Free) – https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.nickzom.nickzomcalculator
Apple (Paid) – https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/nickzom-calculator/id1331162702?mt=8
Once, you have obtained the calculator encyclopedia app, proceed to the Calculator Map, then click on Materials and Metallurgical under Engineering.
Now, Click on Polymer under Materials and Metallurgical
Now, Click on Solubility of Polymer under Polymer
The screenshot below displays the page or activity to enter your values, to get the answer for the solubility of polymer according to the respective parameter which is the Concentration of Diffusing Specie in Polymer (C) and Partial Pressure (P).
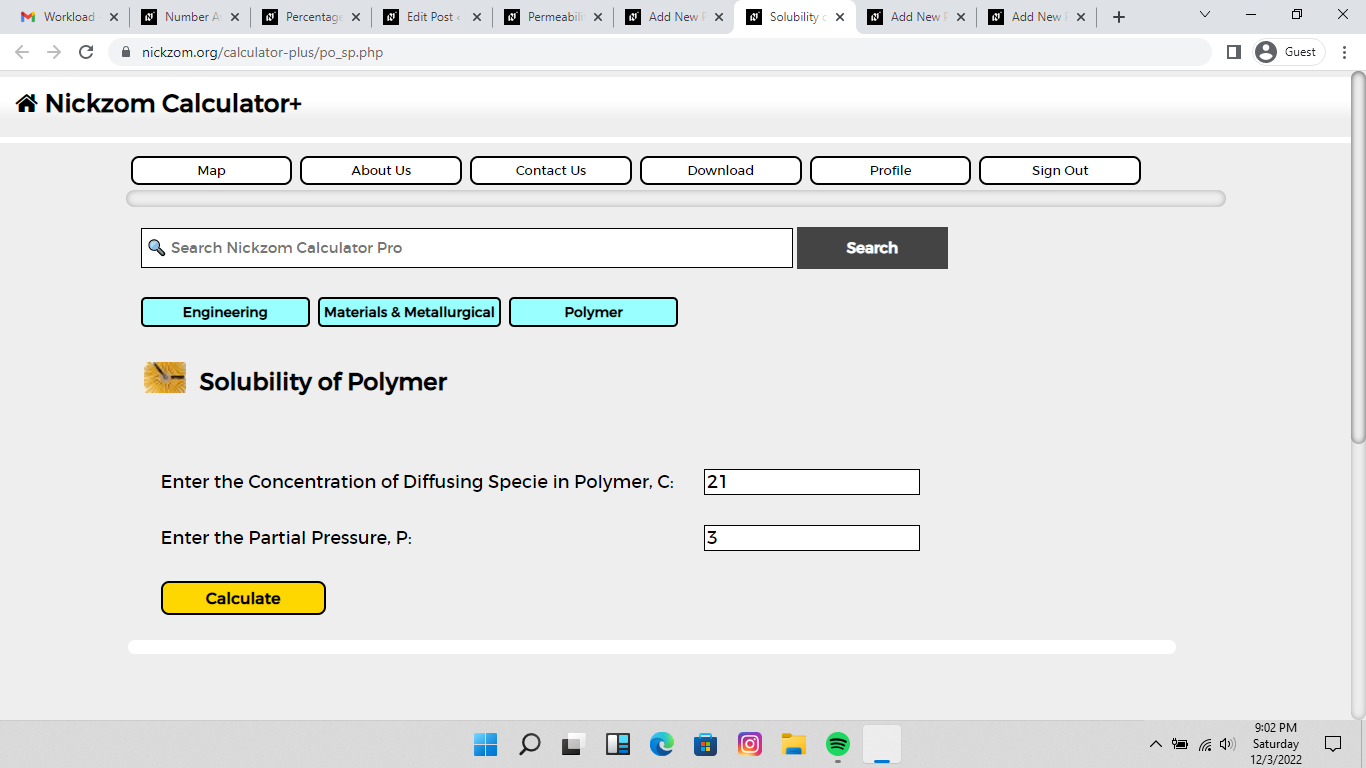
Now, enter the values appropriately and accordingly for the parameters as required by the Concentration of Diffusing Specie in Polymer (C) is 21 and Partial Pressure (P) is 3.
Finally, Click on Calculate
As you can see from the screenshot above, Nickzom Calculator– The Calculator Encyclopedia solves for the solubility of polymer and presents the formula, workings and steps too.